Pollutant Fact Sheets
Sulfur Dioxide
WHAT ARE SULFUR DIOXIDES?
Sulfur dioxide (SO2) is gas formed when fuel containing sulfur, such as coal and oil, is burned.1,2 SO2 is colorless and at high levels has an irritating odor like struck matches. You can be exposed outside if you breathe air that contains SO2.
Combustion sources also emit several other sulfur gases, although the predominant one is SO2. In the atmosphere, SO2 can react with other pollutants, especially in the summer, to form sulfate particles.2 These particles are tiny, and can penetrate deep in the lungs and cause many health effects. These particles can become acidified and cause ‘acid rain.’ This fact sheet focuses on SO2.
WHERE DOES SULFUR DIOXIDE COME FROM?
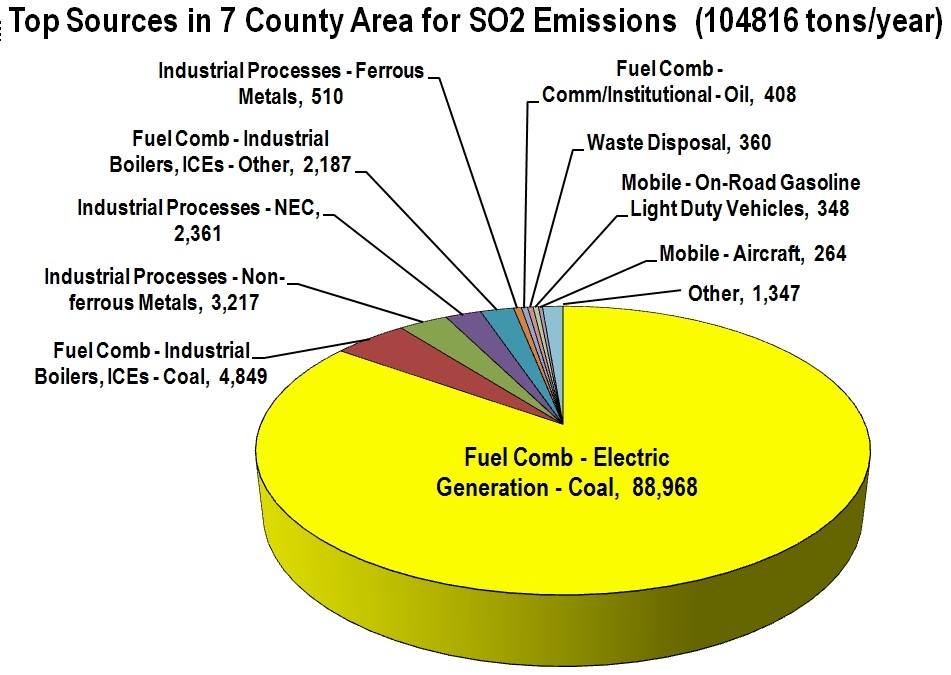
Figure 1: Top Sources for SO2 Emissions in the 7-County Area.
In the southeastern Michigan area (7 counties), SO2 emissions in 2011 were 105,000 tons, equivalent to nearly 12 tons of SO2 emitted each and every hour of the year. Most (85%) of these emissions come from power plants burning coal to produce electricity.3 The largest SO2 emitters are in Monroe, Trenton, and River Rouge. The Monroe plant (shown overleaf) recently has been outfitted with scrubbers that greatly reduce emissions.
The pie chart to the left shows the major sources of SO2 in the southeast Michigan area. These include the DTE coal-fired power plants in Monroe, Trenton Channel and River Rouge, and the US Steel Great Lakes facility in Ecorse.
HOW DOES SULFUR DIOXIDE AFFECT YOUR HEALTH?
Exposure to SO2 has been associated with many serious health concerns. Short term exposure can cause: 2
- Difficulty breathing
- Coughing and shortness of breath
- Irritation of the nose, throat, and lungs
- Stomach pain
- Menstrual disorders
- Watery eyes
- Inhibition of thyroid function
- Loss of smell
- Headaches, nausea, vomiting
- Fever, convulsions, and dizziness
Long Term exposure can cause: 2
- Chronic bronchitis, emphysema, and respiratory illness
- Aggravation of existing heart disease
- Decreased fertility in men and women
Children, the elderly, and people with asthma, cardiovascular disease or chronic lung disease (such as bronchitis or emphysema), are most susceptible to adverse health effects associated with exposure to SO2. 1
WHO IS MOST LIKELY TO BE AFFECTED?
Because most of the SO2 sources are along the Detroit River, people living or working in Southwest Detroit, Ecorse, Trenton, Lincoln Park, and Wyandotte areas have the highest exposure and the greatest risks of negative health effects due to SO2 exposure.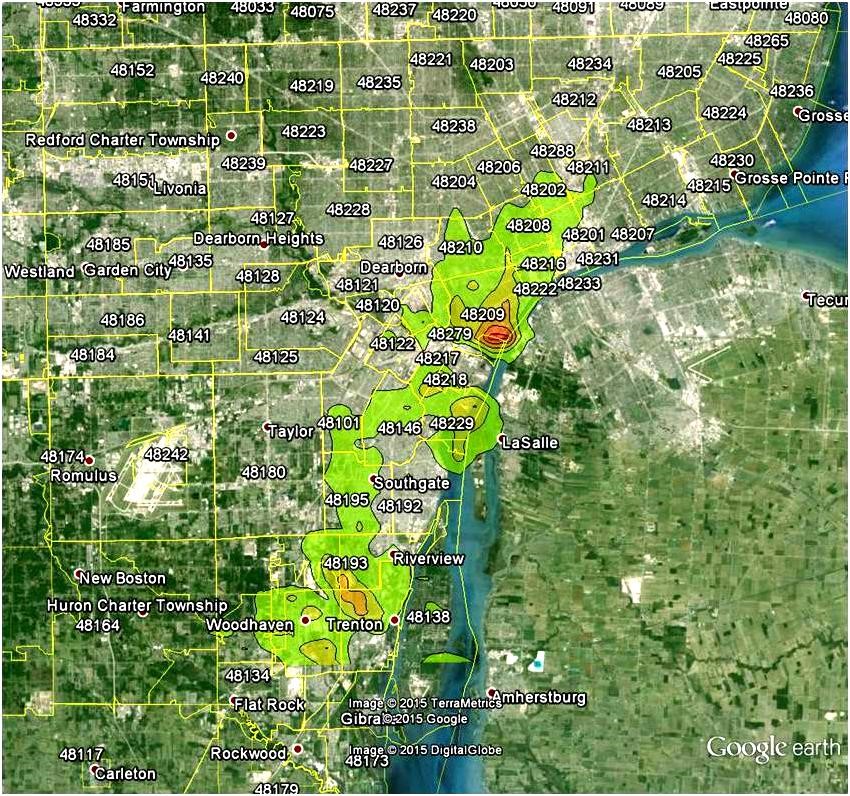
Figure 2: SO2 levels along the Detroit River.
The map above shows the expected higher exposure areas in green, orange and red (in order of increasing SO2 levels). These areas are based on air quality modeling of Detroit-area SO2 sources using allowable emissions. Modeling is used to predict the 4th highest 1-hour concentration, which is the form of the National Ambient Air Quality Standard for SO2.
HOW TO REDUCE AND AVOID EXPOSURE TO SULFUR DIOXIDES
The Michigan Department of Environmental Quality (MDEQ) sets and enforces SO2 ambient standards and emission limits. Petition MDEQ and your local decision makers to lower SO2 emissions from industry, monitor air quality, and meet air quality standards with a margin of safety.
REFERENCES
- Environmental Protection Agency. 2015. Sulfur Dioxide. http://www.epa.gov/airtrends/aqtrnd95/so2.html [accessed 3/3/15]
- U.S. Library of Medicine. 2015. Sulfur Dioxide. http://toxtown.nlm.nih.gov/text_version/chemicals.php?id=29 [accessed 3/3/15]
- National Emissions Inventory. 2011. Sulfur Dioxide. Emissions. http://www.epa.gov/med/grosseile_site/indicators/air-pollution.html [accessed 3/3/15]